- 3 Big Scoops
- Posts
- Portfolio Allocation: 101 💰
Portfolio Allocation: 101 💰
From Warren Buffett to Ivy Leagues
Bulls, Bitcoin, & Beyond
Market Moves Yesterday
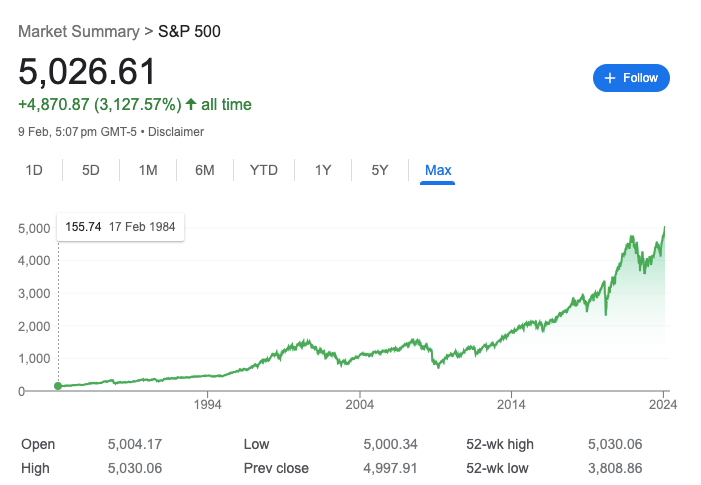
S&P 500 @ 4,894.16 ( ⬆️ 0.53%)
Nasdaq Composite @ 15,510.50 ( ⬆️ 0.18%)
Bitcoin @ $40,109.15 ( ⬆️ 0.55%)
Hey Scoopers,
Happy Wednesday! We are in the midst of a busy week, so let’s take a breather.
In today’s newsletter, we look at the most popular portfolio allocation strategies for the average investor.
So, let’s go 🚀
There are literally hundreds of portfolio strategies out there, from the simplest to the most complex.
Whether you’re looking to get started investing or just want to give your portfolio a refresh, I’ve pulled out six simple approaches that are definitely worth a look.
And to make it easier for you to decide, I’ve compared them head-to-head.
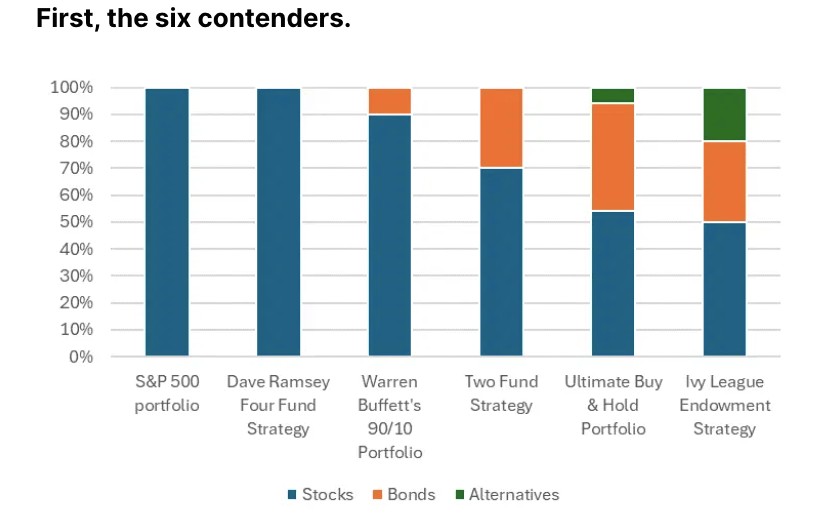
The single-fund portfolio (S&P 500)
This approach makes investing dead easy by putting your money into one all-inclusive fund, usually, a target-date fund that periodically rebalances the mix of asset classes to adjust for risk, but alternatively, a broad market index tracking fund.
Think of this as a “one-stop-shop” for diversification and management of your investments. This approach can be perfect for folks who are new to investing and just want something simple, well-thought-out, and accessible.
But it does have one big drawback: limiting your portfolio to one fund will leave you fully exposed to whatever specific risks it faces. For this analysis, I’ve used the S&P 500 as the single index fund.
Sample portfolio: 100% in stocks via the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (ticker: VOO; expense ratio: 0.03%).
The Two-Fund Portfolio
This strategy embraces the notion that two asset classes are better than one, especially if they’re stocks and bonds. Here, you’d invest in two mutual funds or ETFs: one for stocks and the other for bonds.

This way, you can strike a balance between growing your investment and generating income, all while keeping things straightforward and diversified. It’s a portfolio that lets you spread your bets across riskier stocks and safer bonds in whatever proportions you feel comfortable with.
Sample portfolio: 70% in stocks via the iShares Core S&P US Growth ETF (IUSG; 0.04%) and 30% in bonds via the iShares 7-10 Year Treasury Bond ETF (IEF; 0.15%).
Warren Buffett’s 90/10 Portfolio
This is a pretty simple investment strategy that’s great for anyone who just wants an easy, long-term plan. With this plan, 90% of your money goes into a low-cost S&P 500 index fund, and the remaining 10% goes into short-term government bonds.
Source: Ticker Tape
Buffett’s logic here is that, in the long run, the stock market tends to do better than other investment options. That rationale, plus his consistent confidence in the long-term growth prospects of the US economy, is why his mix goes heavy on stocks and light on bonds.
Sample portfolio: 90% in stocks via the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO; 0.03%) and 10% in bonds via the Vanguard Short-Term Bond ETF (BSV; 0.4%).
Dave Ramsey’s Four-fund Portfolio
Following advice from money expert Dave Ramsey, this plan is about dividing up your investment money into four different types of mutual funds or ETFs: growth, growth and income, aggressive growth, and international.

Because this puts a big chunk of your cash into stocks and includes both aggressive growth and international funds, this strategy is best for investors who can handle the ups and downs of the market and who understand the risks that come with investing in stocks.
Sample portfolio: 100% in stocks, with 25% in each of these
👉 Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (VFIAX; 0.04%)
👉 Vanguard Mid-Cap Index Fund Admiral Shares (VIMAX; 0.05%)
👉 Vanguard Small-Cap Index Fund Admiral Shares (VSMAX; 0.05%) and
👉 Vanguard Total International Stock Index Fund Admiral Shares (VTIAX; 0.11%).
The Ivy League Endowment Portfolio
This investment strategy is the same one used by big-shot university endowments like Harvard, Yale, and Stanford.
These endowments are famous for their fancy investment tactics, which are all about raking in big profits while keeping risk relatively low over the long haul.
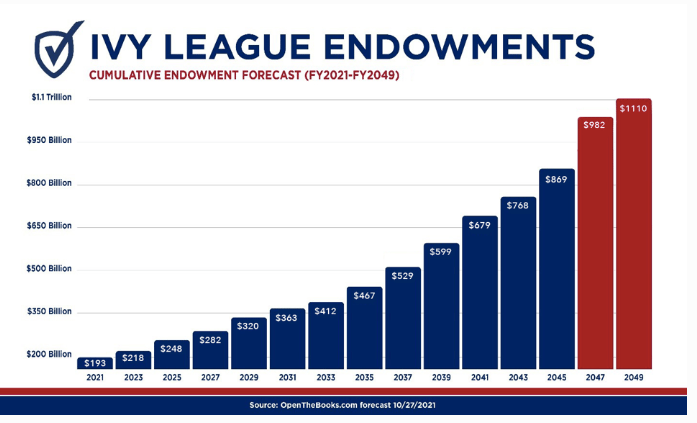
Source: Forbes
Their secret sauce relies on spreading their money out across a mix of stuff, from regular stocks and bonds to alternative investments.
It’s the kind of thing that’s perfect for savvy investors who really get the ins and outs of building and maintaining a diverse portfolio with a hefty chunk of alternative assets.
Sample portfolio: 50% in stocks with:
👉 A 30% weighting in the Vanguard Total Stock Market ETF (VTI; 0.03%)
👉 A 15% weighting in the Vanguard FTSE Developed Markets ETF (VEA; 0.05%) and
👉 A 5% weighting in the iShares MSCI Emerging Markets ETF (EEM; 0.7%)
Then, 30% in bonds, with:
👉 A 15% weighting in the iShares 20+ Year Treasury Bond ETF (TLT; 0.15%)
👉 A 15% weighting in the iShares TIPS Bond ETF (TIP; 0.19%)
The remaining 20% in the Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ; 0.12%)
Ultimate Buy-and-Hold Portfolio
This setup is the most diversified of the bunch: it aims to spread your investments across different types of assets, regions, and investment approaches to boost returns in the long run while keeping risk in check.
The idea is that having a mix of investments from various areas could potentially do a lot better than sticking to one narrow focus.
The specifics of how much goes where might change from investor to investor, but the concept is to hold assets from across categories so that when one asset swings, your whole portfolio is less likely to take a big hit.

Sample portfolio: The composition here mimics the classic 60/40 portfolio, with 54% in stocks, across several ETFs. Another 40% could go to bonds, and the remaining 6% would go to real estate via the Vanguard Real Estate ETF (VNQ; 0.12%).
Here’s What I Found
The popular belief that the more complicated the strategy, the higher the returns is false. Across the six portfolios and across hundreds more analyzed on PortfoliosLab, not many managed to outperform the super-simple S&P 500 index.
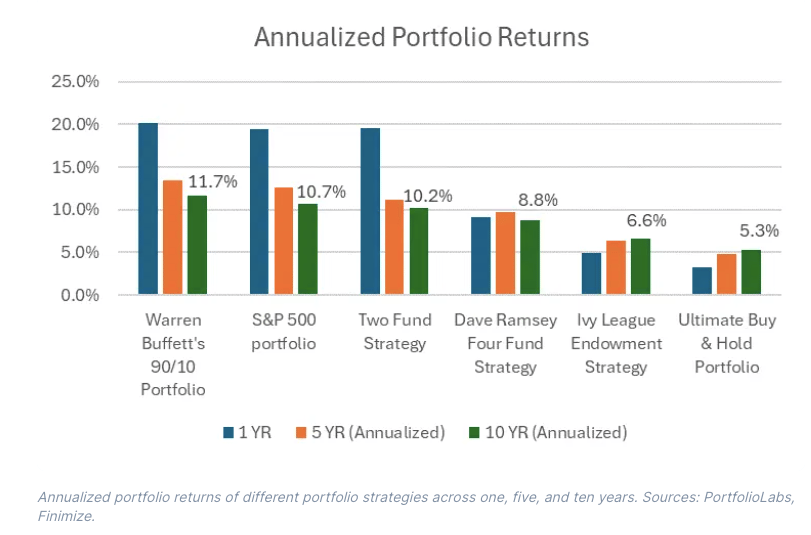
In fact, only Buffett’s 90/10 portfolio managed to outperform the index – and by a commendable annualized 1% over the past decade. I also found that the further the portfolios strayed from the S&P 500, the harder it became to outperform it.
And that makes sense since very few other indexes – from bondland or stockland – have ever managed to beat its returns for any real length of time.
That’s true for portfolio strategies, too: the only ones that have managed to beat the S&P 500 over time were the ones focused predominantly on tech stocks.
No two portfolios are ever the same, and there’s a ton of nuance when you’re comparing one to another. In looking at these various portfolios, I made sure to account for their varying levels of risk by checking out their Sharpe ratios.
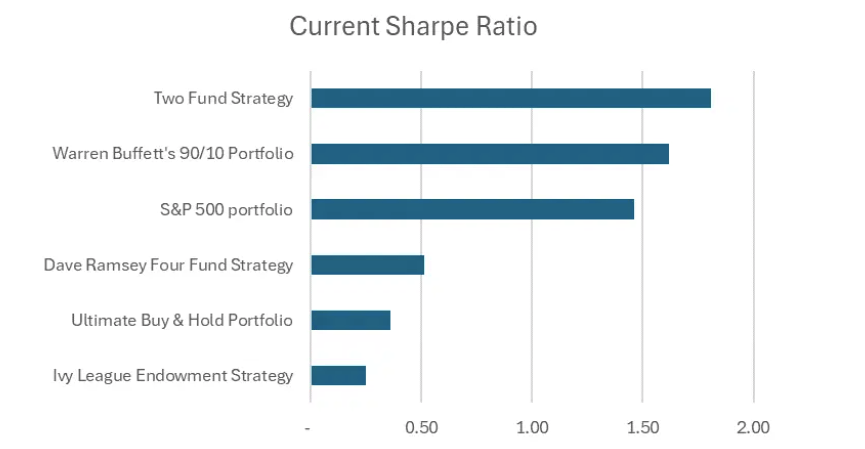
The Sharpe ratio provides insight into how much excess return you receive for the extra volatility that you endure for holding a riskier asset. Essentially, it helps you understand whether the investment’s returns are due to smart investment decisions or a result of excess risk.
A ratio equal to or higher than 1 is considered good, as it reflects a better risk-adjusted performance. Out of our contenders, only two had higher Sharpe ratios than the simple S&P 500 portfolio.
Things to Consider
First, a heads-up about adding in alternative asset classes – for example, with a real estate investment trust or the Vanguard Real Estate ETF.
That move did little to improve the overall returns or risk-adjusted returns of the Ivy League portfolio or the ultimate buy-and-hold portfolio relative to the S&P 500.

In fact, the fund’s higher expense ratio would actually weigh down returns. Still, it’s easy to see the appeal.
It’s one way that retail investors can seek to gain the kind of access that institutional investors have when it comes to alternative assets like private equity, real estate, hedge funds, and commodities, which can help drive impressive performance for those bigger players.
And buying more funds for diversification didn’t necessarily pan out either, in terms of risk-adjusted returns: that much is clear from the ultimate buy-and-hold portfolio.
On the other hand, investing in the S&P 500 alone won’t give you adequate diversification either.
Sure, you’d be investing in 500 companies, but not in equal measures: the top ten companies in the index make up close to a third of the benchmark, with tech companies in eight of the ten positions.
So you might be better off taking a page from Buffett’s playbook and adopting his 90/10 portfolio if that feels right for you.
Remember, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to investing. The best portfolio allocation for you will depend on your unique situation and may change over time as your goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon evolve.
DISCLAIMER: None of this is financial advice. This newsletter is strictly educational and is not investment advice or a solicitation to buy or sell assets or make financial decisions. Please be careful and do your own research.